How to Migrate Microsoft Excel Data to Azure Database
-
Written by
-
Post DateNovember 21, 2025
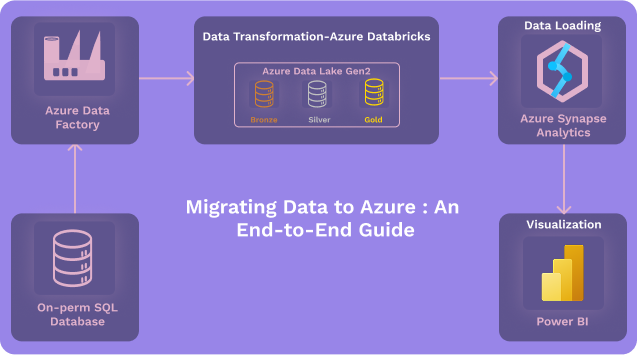
Migrating Excel Data to Azure SQL Database Using Azure Data Factory
Migrating Microsoft Excel data into Azure SQL Database becomes powerful, reliable, and automated when done using Azure Data Factory (ADF).
ADF is Microsoft’s cloud-based ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) service designed to move data from various sources (like Excel files) into Azure services seamlessly.
ADF ensures the migration is scalable, automated, secure, and error-free, making it the best solution for production-grade pipelines.
Below is the complete blog-style explanation with detailed steps.
What is Azure Data Factory?
Azure Data Factory is a cloud-native data integration service that connects, extracts, transforms, and loads data from different sources to various destinations. It supports over 100+ connectors, including Excel, SQL Server, Blob Storage, Data Lake, APIs, and more.
In the context of Excel migration, ADF performs these tasks:

- Reads Excel files from local or cloud storage
- Validates and interprets columns
- Maps data to Azure SQL schema
- Loads the data automatically
- Schedules the pipeline for repeated ingestion
This is ideal for businesses wanting a modern, automated, and cloud-ready data solution.
📌 Step-by-Step Guide: Migrating Excel to Azure SQL Using Azure Data Factory
Step 1: Upload Your Excel File to Azure Storage :
Before ADF can read the file, it must be stored in Azure. Upload your .xlsx file into:
- Azure Blob Storage (recommended) Or
- Azure Data Lake Gen2
Steps:
- 1. Go to Azure Portal
- 2. Open your Storage Account
- 3. Go to Containers
- 4. Create a new container (e.g., excel-files)
- 5. Click Upload → Select your Excel file
This makes the file accessible to Azure Data Factory.
Step 2: Create an Azure Data Factory Instance
Steps:
- 1. Go to Azure Portal
- 2. Click Create a Resource
- 3. Search Data Factory
- 4. Provide:
- 5. Click Create
Step 3: Create Linked Service for Azure Storage
Steps:
- 1. Go to Manage → Linked Services
- 2. Click + New
- 3. Select Azure Blob Storage or Azure Data Lake Gen2
- 4. Enter:
- Storage Account name
- Key Authentication / Managed Identity
- 5. Test Connection → Create
Step 4: Create Linked Service for Azure SQL Database
Steps:
- 1. Again, click New Linked Service
- 2. Select Azure SQL Database
- 3. Enter:
- Server Name
- Database Name
- Username & Password
- 4. Test Connection → Create
Step 5: Create an Excel Dataset (Source Dataset)
Steps:
- 1. Go to Author → Datasets → +New
- 2. Choose Excel
- 3. Select the Linked Service you created
- 4. Browse and select the Excel file
- 5. Configure:
- Sheet name
- First row as header
- Range if needed
Step 6: Create SQL Dataset (Destination Dataset)
Steps:
- 1. Create New Dataset
- 2. Select Azure SQL Database
- 3. Pick the correct Linked Service
- 4. Choose table name
- You can click Auto Create Table if the table doesn’t exist
Step 7: Build the ADF Pipeline
Steps:
- 1. Go to Author → Pipelines → +New Pipeline
- 2. Add a Copy Data activity
- 3. Select the Excel Dataset as Source
- 4. Select the SQL Dataset as Sink
- 5. Configure extra settings (optional):
- Upsert (update & insert)
- Pre-copy script
- Data Formatting
Step 8: Perform Column Mapping
Steps:
- 1. Click Mapping tab
- 2. Match Excel columns → SQL columns
- 3. Convert data types if necessary
- 4. Remove columns you don’t need
Step 9: Run the Pipeline
Steps:
- 1. Click Debug (test run)
- 2. Fix any errors
- 3. Click Publish to save
- 4. Click Trigger Now to start the pipeline
Step 10: Schedule the Pipeline (Optional)
Steps:
- 1. Go to Triggers → + Add
- 2. Choose frequency:
- Daily
- Weekly
- Hourly
- 3. Save and activate
- 4. Now your Excel data will sync automatically on schedule.
This defines the entire process of how to Migrate Excel data to Azure Database workflow.
Start Your Seamless Excel-to-Azure Migration Today
Modernize your data pipeline with automated, scalable, and secure Azure Data Factory workflows.